Incheon Bridge
Dubbed as the “highway over the sea”, the Incheon Bridge is the longest bridge in Korea
Incheon Bridge
Dubbed as the “highway over the sea”, the Incheon Bridge is the longest bridge in Korea.
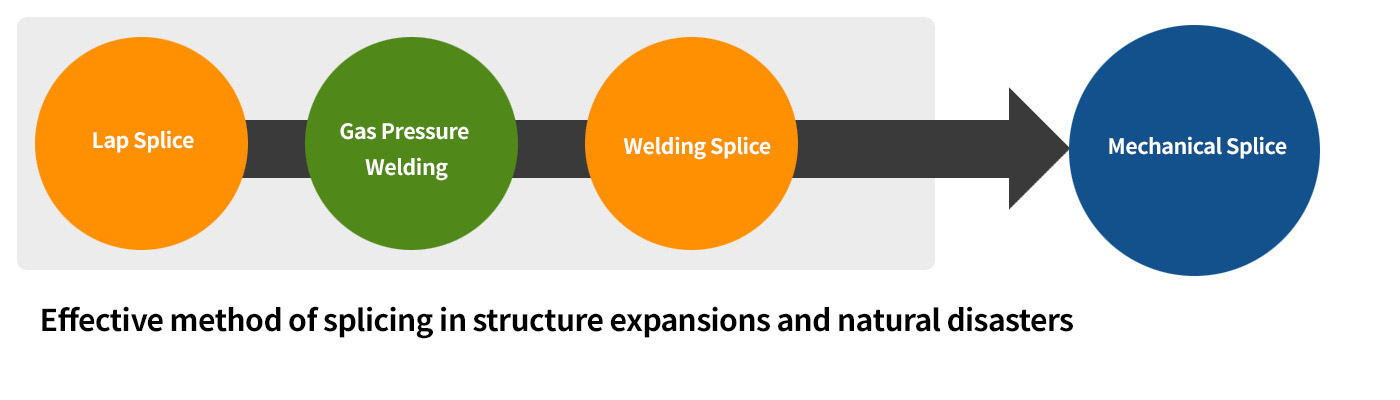
Types of Rebar Splice
Methods of rebar splicing in use largely include lap splice, gas pressure welding splice, welding splice and mechanical splice.
Mechanical splice is the most popular method of splicing for its outstanding effects in recent structure expansions and natural disasters such as an earthquake.
This method has been verified as effective in constructability in many applications.
Methods of splicing rebars in use largely include a lap splice, a gas pressure welding, a welding splice and a mechanical splice.
A mechanical splice is the most popular method of splicing for its outstanding effects in recent structure expansions and natural disasters such as an earthquake.
This method has been verified as effective in workability in many applications.
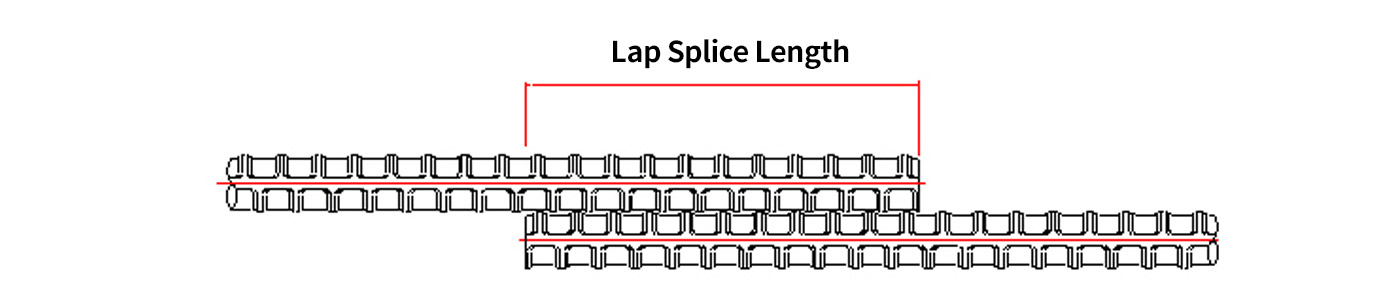
Works as the conventional method of rebar splicing the steel reinforcing bars
The lap splice, which has become the conventional method of rebar splicing, is widely used for its simple construction and economic efficiency. But, recently this method faces many restrictions in its use due to the density of rebars and construction-related problems caused by structure expansions and anti-seismic applications.
In particular, the rebar splice by the lap splice has difficulty performing construction in compliance with a norm of a seam position in the structure’s RC norm. The fracture of concrete by adhesion cracks created in the joint of a concrete members suffers a rapid loss of its strength by the fracture. Therefore, in designing the lap splice, the following should be selected not to generate such an adhesion crack and fracture : the splice position, lap splice length, sheath thickness and gap between rebars.
Works as the traditional method
of connecting the steel reinforcing bars
The lap splice, which has become the traditional method of connecting the steel reinforcing bars, is widely used for its simple construction and economic efficiency. But, recently this method face many restrictions in its use due to the density of rebars and construction-related problems caused by structure expansions and anti-earthquake applications.
In particular, the rebar splice by the lap splice has difficulty performing construction in compliance with a norm of a seam position in the building RC norm. The fracture of concrete by adhesion cracks created in the joint of a concrete member suffers a rapid loss of its strength by the fracture. Therefore, in designing the lap splice, the following should be selected not to generate such an adhesion crack and fracture : the splice position, lap splice length, cover thickness and gap between rebars.
Improved and applied by Japan as a rebar splice method from the U.S. railroad rail splice method, the gas pressure welding splice is divided into manual pressure welding and automated pressure welding.
Developed as a technology used for a railroad rail splice in the U.S., the gas pressure welding is a technology that is applied in Japan to the rebar splice and this technology is no longer used in the U.S. to splice rebar.
The gas pressure welding is a method in which two rebar ends face each other, heating them with oxygen-acetylene gas flames at a temperature of about 1300°C. Then, a pressure is applied to the rebars at a solid state and the splicing is performed by rearranging the positive atom of the mating surfaces.
In gas pressure welding, rearranging atoms on the mating surfaces is difficult if bumps are shown on the mating surfaces. Therefore, construction should be performed after finishing the mating surfaces cleanly with a grinder (Electric Grindstone).
As the gas pressure welding heat the rebar ends locally, a review is needed on the principle of normal temperature processing specified in the heat affected zone of rebar and specification norm (Concrete Standard Specifications – Construction Ch. 10 Building Section’, ACI 318-318R Ch. 7 -3).
Most of all, reinforcing bars (SD400 or above) is made from high carbon and high manganese steel, which therefore may cause a vulnerability to occur following the pressure welding. It also lowers the intensity of rebar manufactured through the tempcore process, which therefore requires a thorough quality control.
Improved and applied by Japan as a rebar splice method from the U.S. railroad rail splice method, the gas pressure welding is divided into manual pressure welding and automated pressure welding.
Developed as a technology used for a railroad rail splice in the U.S., the gas pressure welding is a technology that is applied in Japan to the rebar and this technology is no longer used in the U.S. to splice rebar.
The gas pressure welding is a method in which two rebar ends face each other, heating them with oxygen-acetylene gas flames at a temperature of about 1300°C. Then, a pressure is applied to the rebars at a solid state and the splicing is performed by rearranging the positive atom of mating surfaces.
In gas pressure welding, rearranging atoms in mating surfaces is difficult if bumps are shown in mating surfaces. Therefore, construction should be performed after finishing the mating surfaces cleanly with a grinder (Electric Grindstone).
As the gas pressure welding heat the rebar ends locally, a review is needed on the principle of room temperature processing specified in the heat affected zone of rebar and specification norm (Concrete Standard Specifications – Construction Ch. 10 Building Section’, ACI 318-318R Ch. 7 -3).
Most of all, reinforcing bars (SD400 or above) is made from high carbon and high manganese steel, which therefore may cause a vulnerability to occur following the pressure welding. It also lowers the intensity of rebar manufactured through the tempcore process, which therefore requires a thorough quality control.
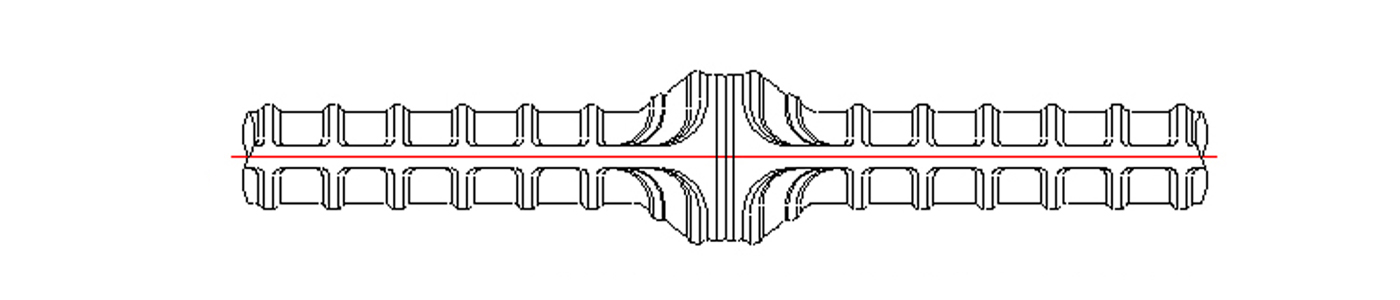
Fusion splicing with two overlaid of rebars
Welding splice rebar is a method of splicing by melting rebars flexibly with the thermal source of energy. This method consists of a mixed iron area where rebar ends and a welding rod melt and a iron area which is heat affected by the welding heat.
As the rebar is heated at high temperatures in welding splice, the iron is heated and oxidized enough to burn a small amount of elements (Carbon, Manganese) contained in the rebar. This results in lowering the strength and toughness.
Above all, the welding splice applied in the construction site shows a decrease in splice reliability and provides challenges in safety and quality control.
Fusion splicing with two overlays
of reinforcing bars
Welding of reinforcing bars in making splices is a method of splicing by melting rebars flexibly with the thermal source of energy. This method consists of a mixed rebar area where rebar ends and a welding rod melt and a steel area which is heat affected by the welding heat.
As the bar is heated at high temperatures in welding splice, the steel is heated and oxidized enough to burn a small amount of atom (Carbon, Manganese) contained in the rebar. This results in lowering the strength and toughness.
Above all, the welding splice applied in the construction site shows a decrease in joint reliability and provides challenges in safety and quality control.

CEO : Se Hyun Jeong | Business Registration Number : 211-86-49984 |Email : bms211@chol.com
Head Office : B-1314, 201, Songpa-daero, Songpa-gu, Seoul, Korea |Tel : + 82 2-549-0675 | Fax : +82 2-549-0677
Chungju Factory : 165, Chungjusandan 2-ro, Chungju-si, Chungcheongbuk-do, Korea | Tel : +82 43-856-6640~2 |Fax : +82 43-856-6643 | Privacy Officer : Hyun-Ki Yoon, Manager
COPYRIGHT © 2022 BOOWON BMS.CO.,Ltd. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.


CEO : Se Hyun Jeong
Business Registration Number : 211-86-49984
Email : bms211@chol.com
Head Office: #1314, Building B, Terra Tower 2, 201 Songpa-daero, Songpa-gu, Seoul, Korea
Tel: 02-549-0675 | Fax : 02-549-0677
Chungju Plant : 165, Chungju 2-sandan-ro, Chungju-si, Chungcheongbuk-do, Korea
Tel : 043-856-6640~2 |Fax : 043-856-6643
Personal Profile Manager: Hyun-Ki Yoon, Deputy Head of Department
COPYRIGHT © 2022 BOOWON BMS ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
다운로드 전에 아래 정보를 입력해 주세요.

GLOBAL NO.1 in the specialized mechanical rebar splice with a competitive advantage
in technology and a creative passion
Head Office : 02-549-0675
Chungju Plant : 043-856-6640~2

경쟁력 있는 기술과 창조적 열정으로
기계적 철근이음 전문분야 GLOBAL NO.1
시공응용